法线和切线¶
G-buffer 法线编码¶
如果将法线的 XYZ 分量直接存进 R8G8B8A8 G-buffer 的 RGB 通道中,会损失很多精度,光照结果有明显的瑕疵。
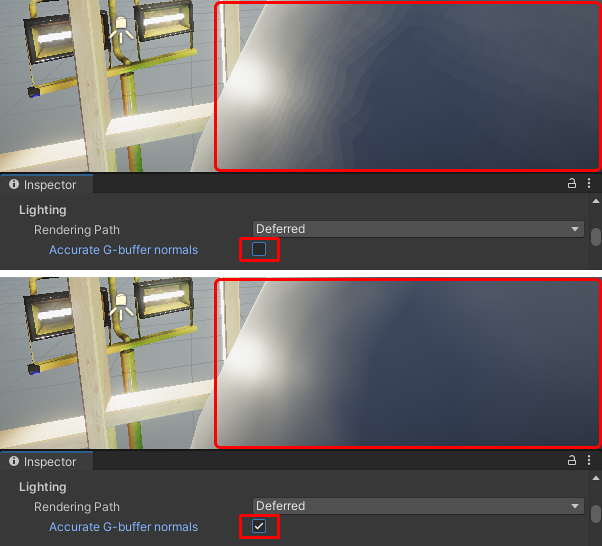
在 Unity 中启用 Accurate G-buffer normals 会切换到八面体(Octahedron)编码,提高法线的准确度,代价是增加了一点计算量。流程是
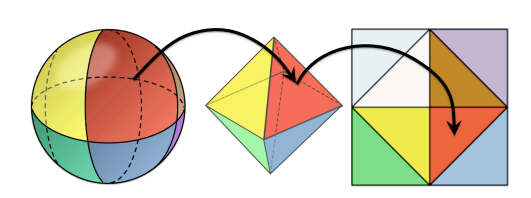
- 法线是一个单位向量,可以看成单位球上的点
- 将单位球上的点都投影到八面体上
- 将八面体投影到正方形上
- 将正方形坐标范围变为 \([0,1]^2\),将坐标存进 G-buffer
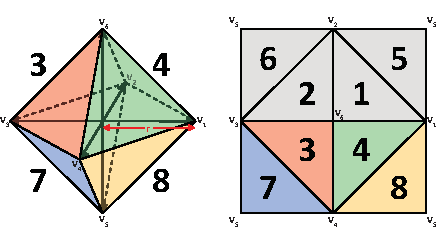
八面体的上半部分投影在正方形内部,下半部分投影在正方形四个角上。
八面体的方程为
它的中心为 \((0,0,0)\),外接圆半径为 \(1\)。将任意一点 \((x,y,z)\) 投影到八面体的表面得到
假设竖着的是 \(z\) 轴,接下来把点投影到正方形上
- 如果 \(z' \ge 0\),点被投影到正方形内部,直接使用 \((x',y')\) 就行
-
如果 \(z'<0\),点被投影到正方形四个角上,方法不唯一,常用的是
float2 output = (1.0 - abs(input.xy)) * sign(input.xy);
最后把 output 从 \([-1,1]^2\) 变成 \([0,1]^2\) 就能存进 G-buffer 了。
// Ref: https://github.com/Unity-Technologies/Graphics/blob/master/Packages/com.unity.render-pipelines.core/ShaderLibrary/Packing.hlsl
// Ref: http://jcgt.org/published/0003/02/01/paper.pdf "A Survey of Efficient Representations for Independent Unit Vectors"
// Encode with Oct, this function work with any size of output
// return float between [-1, 1]
float2 PackNormalOctQuadEncode(float3 n)
{
//float l1norm = dot(abs(n), 1.0);
//float2 res0 = n.xy * (1.0 / l1norm);
//float2 val = 1.0 - abs(res0.yx);
//return (n.zz < float2(0.0, 0.0) ? (res0 >= 0.0 ? val : -val) : res0);
// Optimized version of above code:
n *= rcp(max(dot(abs(n), 1.0), 1e-6));
float t = saturate(-n.z);
return n.xy + float2(n.x >= 0.0 ? t : -t, n.y >= 0.0 ? t : -t);
}
float3 UnpackNormalOctQuadEncode(float2 f)
{
// NOTE: Do NOT use abs() in this line. It causes miscompilations. (UUM-62216, UUM-70600)
float3 n = float3(f.x, f.y, 1.0 - (f.x < 0 ? -f.x : f.x) - (f.y < 0 ? -f.y : f.y));
//float2 val = 1.0 - abs(n.yx);
//n.xy = (n.zz < float2(0.0, 0.0) ? (n.xy >= 0.0 ? val : -val) : n.xy);
// Optimized version of above code:
float t = max(-n.z, 0.0);
n.xy += float2(n.x >= 0.0 ? -t : t, n.y >= 0.0 ? -t : t);
return normalize(n);
}
八面体编码后只有两个分量,Unity 将两个分量存进 RGB 3 个通道中,每个分量占 12 位。
// Pack float2 (each of 12 bit) in 888
uint3 PackFloat2To888UInt(float2 f)
{
uint2 i = (uint2) (f * 4095.5);
uint2 hi = i >> 8;
uint2 lo = i & 255;
// 8 bit in lo, 4 bit in hi
uint3 cb = uint3(lo, hi.x | (hi.y << 4));
return cb;
}
// Pack float2 (each of 12 bit) in 888
float3 PackFloat2To888(float2 f)
{
return PackFloat2To888UInt(f) / 255.0;
}
// Unpack 2 float of 12bit packed into a 888
float2 Unpack888UIntToFloat2(uint3 x)
{
// 8 bit in lo, 4 bit in hi
uint hi = x.z >> 4;
uint lo = x.z & 15;
uint2 cb = x.xy | uint2(lo << 8, hi << 8);
return cb / 4095.0;
}
// Unpack 2 float of 12bit packed into a 888
float2 Unpack888ToFloat2(float3 x)
{
uint3 i = (uint3) (x * 255.5); // +0.5 to fix precision error on iOS
return Unpack888UIntToFloat2(i);
}
Shadertoy 上有演示程序,右上角的数字是保存两个分量使用的总 bits 数
参考
- 3d - What is Octahedral Compression of Vertex Arrays? - Stack Overflow
- Octahedron normal vector encoding | Krzysztof Narkowicz
- A Survey of Efficient Representations for Independent Unit Vectors(原始论文)
常见的还有球坐标编码,但是涉及较多三角函数计算,性能不太好。
切线计算¶
正经项目中应该使用 MikkTSpace,这里只记录基本的数学原理。
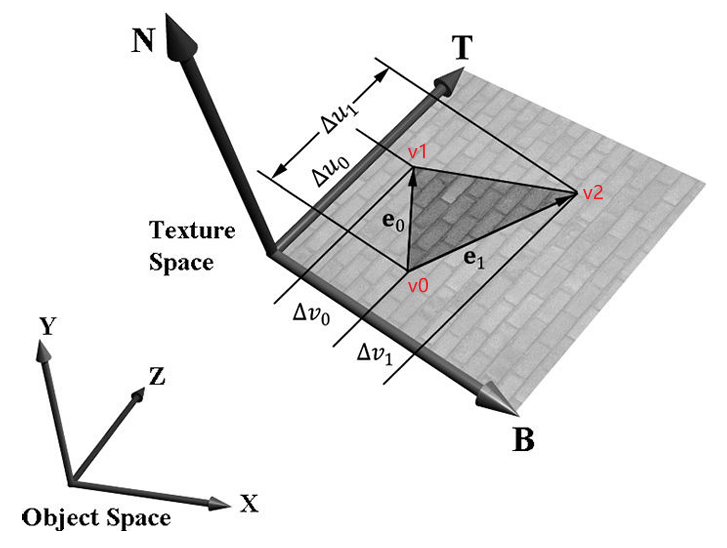
上图中,三角形的三个顶点为 \(\mathbf{v}_0,\mathbf{v}_1,\mathbf{v}_2\)。规定每个顶点的 tangent 和 u 轴方向一致,bitangent 和 v 轴方向一致,那么
其中
所以
伪代码
for (Triangle& tri : triangles)
{
Vertex& v0 = Vertices[tri.index0];
Vertex& v1 = Vertices[tri.index1];
Vertex& v2 = Vertices[tri.index2];
float3 dp0 = v1.position - v0.position;
float3 dp1 = v2.position - v0.position;
float2 duv0 = v1.uv - v0.uv;
float2 duv1 = v2.uv - v0.uv;
float rcpDet = 1.0f / (duv0.x * duv1.y - duv1.x * duv0.y);
float3 t = (duv1.y * dp0 - duv0.y * dp1) * rcpDet;
float3 b = (duv0.x * dp1 - duv1.x * dp0) * rcpDet;
v0.tangent.xyz += t;
v1.tangent.xyz += t;
v2.tangent.xyz += t;
bitangents[tri.index0] += b;
bitangents[tri.index1] += b;
bitangents[tri.index2] += b;
}
for (int i = 0; i < vertexCount; i++)
{
Vertex& v = Vertices[i];
float3 n = v.normal;
float4 t = v.tangent;
float3 b = bitangents[i];
// Gram-Schmidt orthogonalize
t.xyz = normalize(t.xyz - n * dot(n, t.xyz));
// Calculate handedness
t.w = dot(cross(n, t.xyz), b) < 0.0f ? -1.0f : 1.0f;
v.tangent = t;
}
一个顶点可能被多个三角形共用,要把这些三角形对应的切线都算出来,然后求平均。求平均后,法线和切线可能不正交,所以要做施密特正交化。切线的 w 分量用来记录坐标系的手性,在 shader 中用下面的公式还原 bitangent
如果 \(\mathbf{T},\mathbf{B},\mathbf{N}\) 都在 Object Space,可以用下面的矩阵将 Tangent Space 的点变换到 Object Space
\(\mathbf{M}_{\text{object}}\) 是一个正交矩阵,所以从 Object Space 到 Tangent Space 的变换矩阵为
参考
- Computing Tangent Space Basis Vectors for an Arbitrary Mesh - Eric Lengyel
- textures - How to compute tangent and bitangent vectors - Game Development Stack Exchange
- DirectX 12 3D 游戏开发实战
法线贴图采样¶
float3 normalTS = _BumpMap.Sample(sampler_BumpMap, input.uv).xyz * 2.0 - 1.0;
normalTS.xy *= _BumpScale;
normalTS = normalize(normalTS);
float3 N = normalize(input.normalWS);
float3 T = normalize(input.tangentWS.xyz - dot(input.tangentWS.xyz, N) * N);
float3 B = cross(N, T) * input.tangentWS.w;
float3 bumpedNomalWS = normalize(mul(normalTS, float3x3(T, B, N))); // float3x3() 是行主序矩阵
法线贴图压缩¶
双通道¶
Normal Map 保存的是 TBN 空间下的归一化法线,z 分量是大于 0 的(接近 1),所以可以只保存 x 和 y 分量。1
z 分量用下面的公式就能算出:
// x、y 分别存在 r、g 通道
float3 normalTBN = float3(normalMap.rg, 0);
normalTBN.z = sqrt(1 - dot(normalTBN.xy, normalTBN.xy));
球极投影¶
双通道保存是以精度为代价的。主要是 gpu 插值的原因。