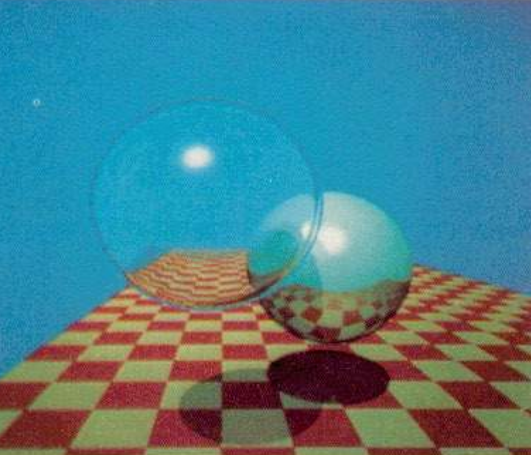
光线追踪¶
光栅化的速度快,但质量差。光线追踪质量好,但速度慢。
Light Rays¶
对光线的三个假设(物理上存在一些错误)
- 光沿直线传播
- 两束光相遇后,不会发生碰撞,继续各自朝原来的方向传播
- 光路可逆。光从光源出发传播到眼睛,但如果把路径反过来,物理相关的计算也不会变
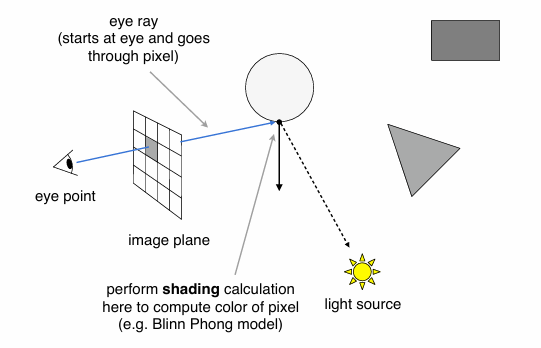
进行光线追踪时,总是从眼睛发出光线,然后击中物体和光源。
Ray Casting¶
使用类似小孔呈像的思路
- 从眼睛往图像的每个像素发出一条射线
- 从场景里被击中的点往光源发出一条射线,检查该点是否被遮挡
- 计算光照
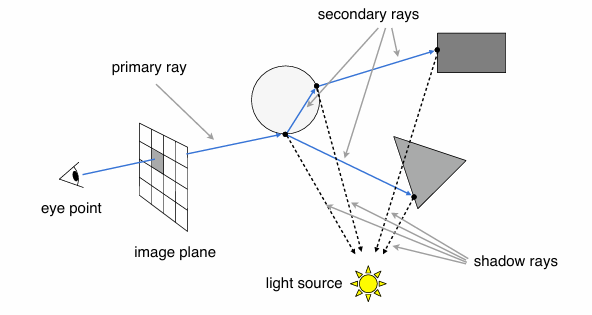
Whitted-Style Ray Tracing¶
从眼睛朝某像素发出第一条射线(primary ray),击中物体后发生反射和折射,产生 secondary rays,继续击中其他物体。从每个被击中的点向光源发出一条射线(shadow ray),检查是否被遮挡。像素颜色是所有被击中的点的光照结果之和。
所有反射都是理想的镜面反射,所有折射都是理想的折射,且遇到漫反射表面就停止 bouncing,渲染结果不真实。
Problem 1: The Utah teapot¶
Always perform specular reflections/refractions. Where should the ray be reflected for glossy materials?
Whitted-Style Ray Tracing 只进行镜面反射,所以只能得到左边的结果。现实中的茶壶不是完全镜面,应该是右边这样。
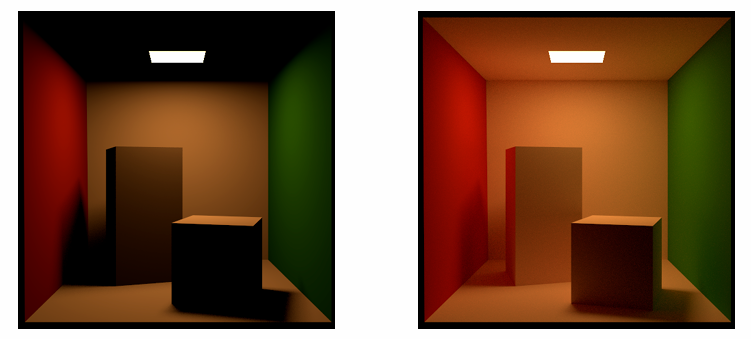
Problem 2: The Cornell box¶
Stop bouncing at diffuse surfaces. No reflections between diffuse materials?
Whitted-Style Ray Tracing 在漫反射表面停止反射,只能得到左边的结果。现实中应该是右边这样。
Monte Carlo Path Tracing¶
Path Tracing 基于 渲染方程,可以使用 蒙特卡罗方法 近似求解。
Direct Illumination Only¶
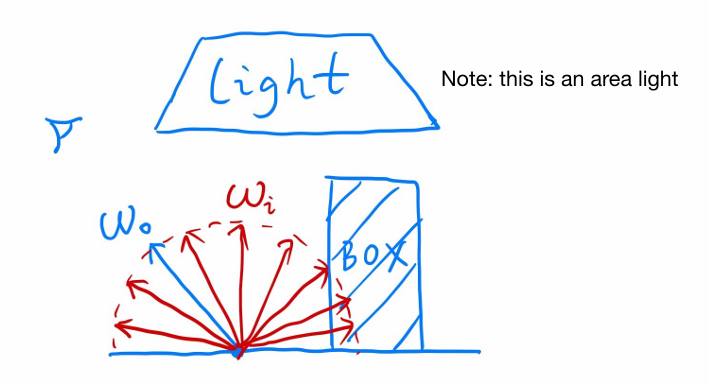
Suppose we want to render one pixel (point) in the following scene for direct illumination only.
忽略该点的自发光的话,只要用 Monte Carlo 方法求解一个反射方程即可。
其中随机变量 \(\omega_{i_k} \sim pdf(\omega_i)\),伪代码
shade(p, wo)
Randomly choose N directions wi~pdf
Lo = 0.0
For each wi
Trace a ray r(p, wi)
If ray r hit the light
Lo += (1 / N) * L_i * f_r * cosine / pdf(wi)
Return Lo
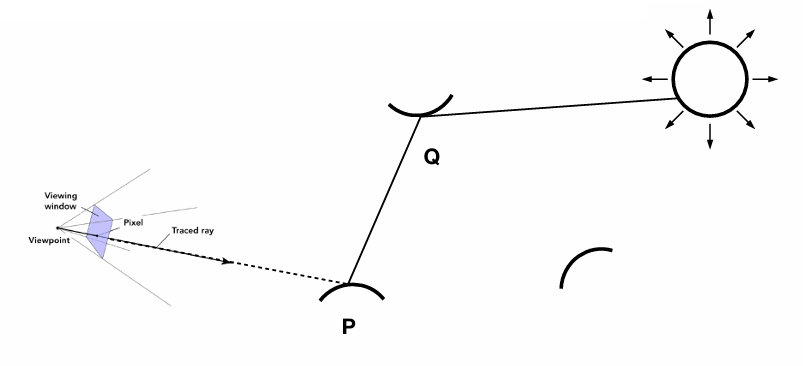
Global Illumination¶
进一步,如果我们在 \(P\) 点追踪的光线击中物体 \(Q\),只要把 \(Q\) 当作光源即可。\(Q\) 的等效 L_i 就是 shade(q, -wi)。
shade(p, wo)
Randomly choose N directions wi~pdf
Lo = 0.0
For each wi
Trace a ray r(p, wi)
If ray r hit the light
Lo += (1 / N) * L_i * f_r * cosine / pdf(wi)
+ Else If ray r hit an object at q
+ Lo += (1 / N) * shade(q, -wi) * f_r * cosine / pdf(wi)
Return Lo
Path Tracing¶
shade(p, wo) 是一个递归函数,它在开始的时候会进行 \(N\) 次随机采样,随着递归深度增加,发出的光线数量是 \(N\) 的指数级别,计算量直接爆炸。
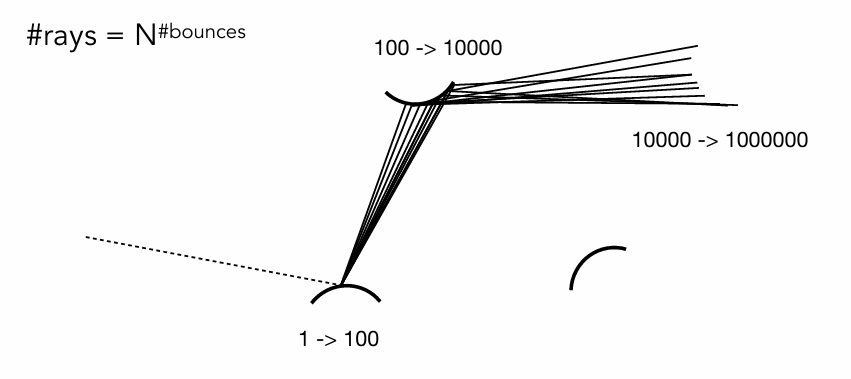
解决方法是令 \(N=1\)。
shade(p, wo)
Randomly choose ONE direction wi~pdf
Trace a ray r(p, wi)
If ray r hit the light
Return L_i * f_r * cosine / pdf(wi)
Else If ray r hit an object at q
Return shade(q, -wi) * f_r * cosine / pdf(wi)
这就是一次 Path Tracing。另外,如果 \(N \ne 1\),对应的算法叫 Distributed Ray Tracing。
Ray Generation¶
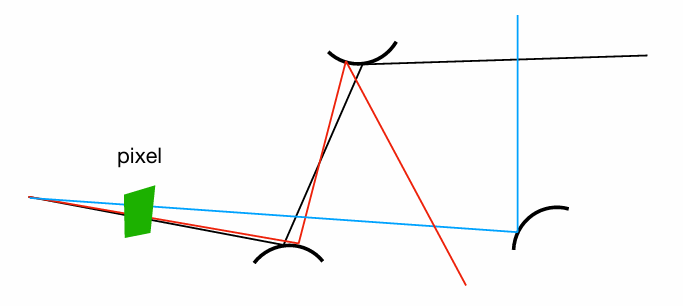
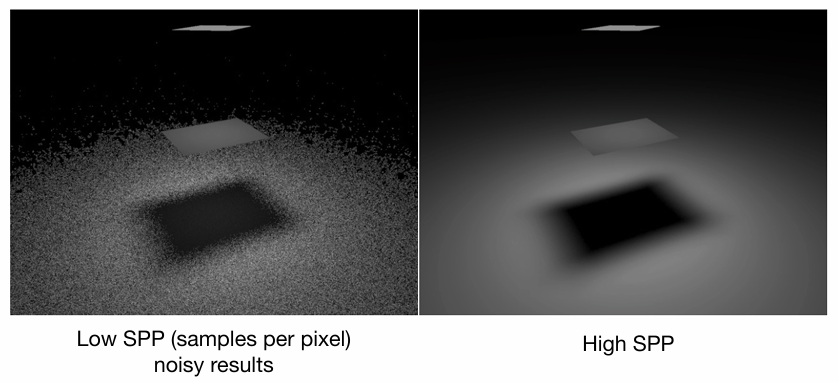
一次 Path Tracing 的噪声较多,所以针对每个像素,进行 \(N\) 次 Path Tracing 然后取平均值。\(N\) 被称为 SPP(Samples Per Pixel)。
上图进行了红、蓝、黑三次 Path Tracing。
ray_generation(camPos, pixel)
Uniformly choose N sample positions within the pixel
pixel_radiance = 0.0
For each sample in the pixel
Shoot a ray r(camPos, cam_to_sample)
If ray r hit the scene at p
pixel_radiance += 1 / N * shade(p, sample_to_cam)
Return pixel_radiance
Russian Roulette (RR)¶
shade(p, wo) 是一个递归函数,还要给它加一个终止条件。然而,现实中的光在不停地 bouncing,提前结束 bouncing 意味着丢失光剩余的能量。

之前每次 shade(p, wo) 都会发射一条光线并返回结果 \(L_o\),现在利用俄罗斯轮盘赌的思想,有 \(0<P<1\) 的概率发射一条光线并返回结果 \(\dfrac{L_o}{P}\),有 \(1-P\) 的概率直接返回 \(0\)。这个算法不会改变 shade(p, wo) 结果的数学期望
现在 shade(p, wo) 不会无限递归了。
shade(p, wo)
+ Manually specify a probability P_RR
+ Randomly select ksi in a uniform dist. in [0, 1]
+ If (ksi > P_RR) return 0.0;
+
Randomly choose ONE direction wi~pdf
Trace a ray r(p, wi)
If ray r hit the light
- Return L_i * f_r * cosine / pdf(wi)
+ Return L_i * f_r * cosine / pdf(wi) / P_RR
Else If ray r hit an object at q
- Return shade(q, -wi) * f_r * cosine / pdf(wi)
+ Return shade(q, -wi) * f_r * cosine / pdf(wi) / P_RR
Sampling the Light¶
渲染方程是对立体角微元 \(\mathrm{d}\omega\) 的积分,所以之前的算法会均匀采样 Shading Point 的上半球,但这样效率较低。
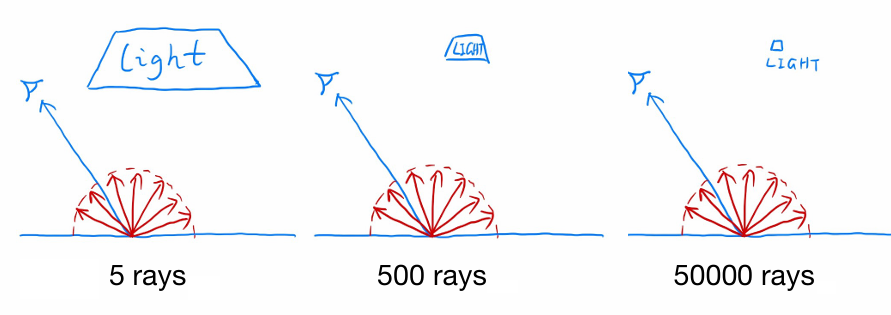
上图左边每发出 5 条射线有 1 条击中光源,中间每 500 条有 1 条,右边每 50000 条有 1 条,很多射线都是无效的。
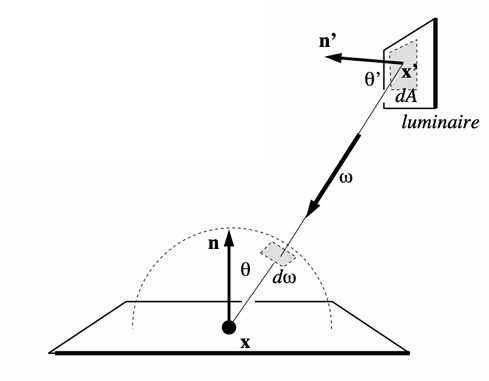
解决方法是将 \(\mathrm{d}\omega\) 换元为面光源上的面积微元 \(\mathrm{d}A\),直接对光源积分。
根据立体角定义,将 \(\mathrm{d}A\) 投影到 \(\omega\) 方向的球面,然后除以半径平方得到 \(\mathrm{d}\omega\)
带回渲染方程(忽略自发光)
Previously, we assume the light is "accidentally" shot by uniform hemisphere sampling. Now we consider the radiance coming from two parts:
- light source (direct, no need to have Russian Roulette)
- other reflectors (indirect, Russian Roulette)
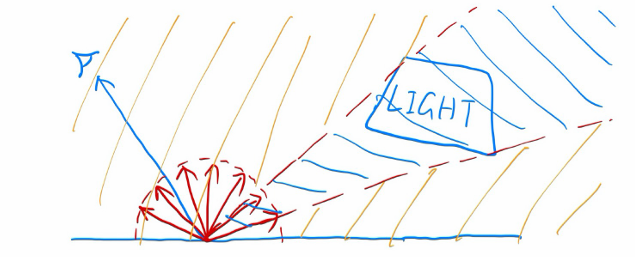
再考虑光源被遮挡的情况,最终的伪代码如下
shade(p, wo)
# Contribution from the light source.
L_dir = 0.0
Uniformly sample the light at x’~pdf_light
Shoot a ray from p to x’
If the ray is not blocked in the middle
L_dir = L_i * f_r * cos θ * cos θ’ / |x’ - p|^2 / pdf_light(x')
# Contribution from other reflectors.
L_indir = 0.0
Test Russian Roulette with probability P_RR
Uniformly sample the hemisphere toward wi~pdf_hemi
Trace a ray r(p, wi)
If ray r hit a non-emitting object at q
L_indir = shade(q, -wi) * f_r * cos θ / pdf_hemi(wi) / P_RR
Return L_dir + L_indir
Path Tracing is almost 100% correct, a.k.a. PHOTO-REALISTIC.
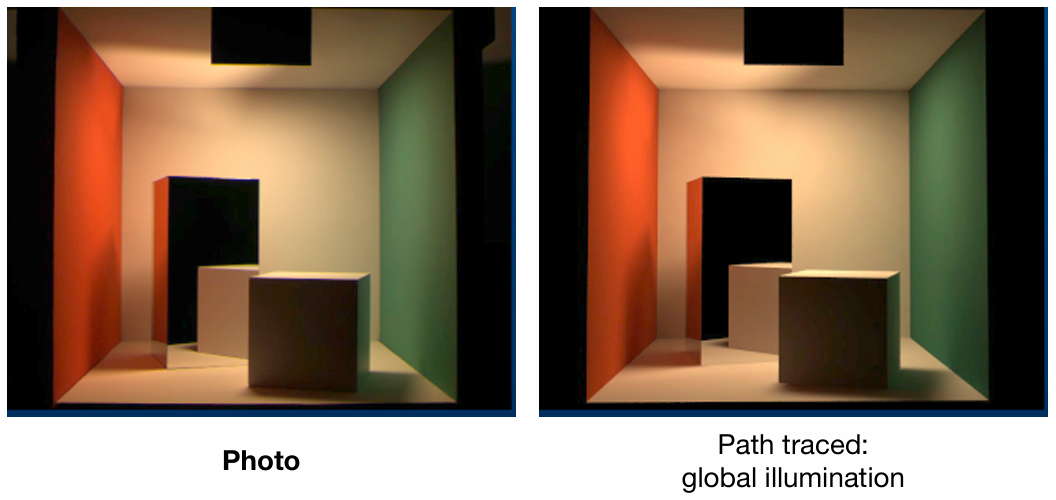

More¶
- Uniformly sampling the hemisphere
- How? And in general, how to sample any function? (sampling)
- Monte Carlo integration allows arbitrary pdfs
- What's the best choice? (importance sampling)
- Do random numbers matter?
- Yes! (low discrepancy sequences)
- I can sample the hemisphere and the light
- Can I combine them? Yes! (multiple imp. sampling)
- The radiance of a pixel is the average of radiance on all paths passing through it
- Why? (pixel reconstruction filter)
- (Unidirectional & bidirectional) path tracing
- Photon mapping
- Metropolis light transport
- VCM / UPBP