字符串排序¶
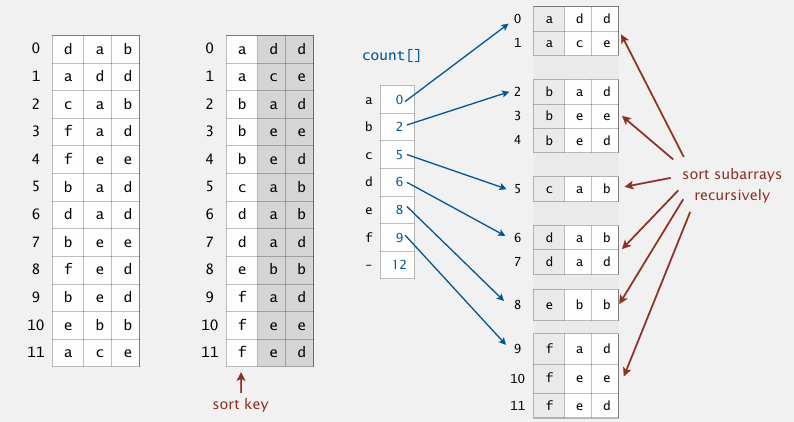
Key-Indexed Counting¶
用于排序一组字符,例如字符串内部的字符。
- 利用
count数组统计字符个数,注意保证count[0] == 0,计数值要从count[1]开始保存 - 算前缀和,得到每种字符的起始位置
- 将字符重新填入字符串
假设 a 为字符串,所有字符值都在 [0, R) 内。
int N = a.length;
int R = 256; // extend ASCII alphabet size
String[] aux = new String[N];
// compute frequency counts
int[] count = new int[R+1];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
count[a[i]+1]++;
// compute cumulates
for (int r = 0; r < R; r++)
count[r+1] += count[r];
// move data
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
aux[count[a[i]]++] = a[i];
// copy back
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
a[i] = aux[i];
- 时间复杂度:\(O(N+R)\)
- 空间复杂度:\(O(N+R)\)
LSD Radix Sort¶
用于排序多个字符串,从右到左(低位优先),对每一列字符进行 key-indexed couting,然后调整字符串顺序。
public class LSD {
public static void sort(String[] a, int w) {
int n = a.length;
int R = 256; // extend ASCII alphabet size
String[] aux = new String[n];
for (int d = w-1; d >= 0; d--) {
// sort by key-indexed counting on dth character
// compute frequency counts
int[] count = new int[R+1];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
count[a[i].charAt(d) + 1]++;
// compute cumulates
for (int r = 0; r < R; r++)
count[r+1] += count[r];
// move data
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
aux[count[a[i].charAt(d)]++] = a[i];
// copy back
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
a[i] = aux[i];
}
}
}
MSD Radix Sort¶
用于排序多个字符串,从左到右(高位优先),对每一列字符进行 key-indexed couting,然后调整字符串顺序。
public class MSD {
private static final int R = 256; // extended ASCII alphabet size
private static final int CUTOFF = 15; // cutoff to insertion sort
// return dth character of s, -1 if d = length of string
private static int charAt(String s, int d) {
assert d >= 0 && d <= s.length();
if (d == s.length()) return -1;
return s.charAt(d);
}
public static void sort(String[] a) {
int n = a.length;
String[] aux = new String[n];
sort(a, 0, n-1, 0, aux);
}
// sort from a[lo] to a[hi], starting at the dth character
private static void sort(String[] a, int lo, int hi, int d, String[] aux) {
// cutoff to insertion sort for small subarrays
if (hi <= lo + CUTOFF) {
insertion(a, lo, hi, d);
return;
}
// compute frequency counts
int[] count = new int[R+2];
for (int i = lo; i <= hi; i++) {
int c = charAt(a[i], d);
count[c+2]++;
}
// transform counts to indices
for (int r = 0; r < R+1; r++)
count[r+1] += count[r];
// distribute
for (int i = lo; i <= hi; i++) {
int c = charAt(a[i], d);
aux[count[c+1]++] = a[i];
}
// copy back
for (int i = lo; i <= hi; i++)
a[i] = aux[i - lo];
// recursively sort for each character (excludes sentinel -1)
for (int r = 0; r < R; r++)
sort(a, lo + count[r], lo + count[r+1] - 1, d+1, aux);
}
}
按当前列排序好后,最后一个 for 循环会按这一列的字符分组递归。这一列字符相同的字符串会被分到一组,然后根据后一列排序。
- 如果拆分的
subarray都很小,效率会变低,所以subarray长度足够小时,改用插入排序 - 如果相同字符串较多,性能也不好
- 如果字符串不一样长,可以在字符串后面补
-1,参考charAt()方法
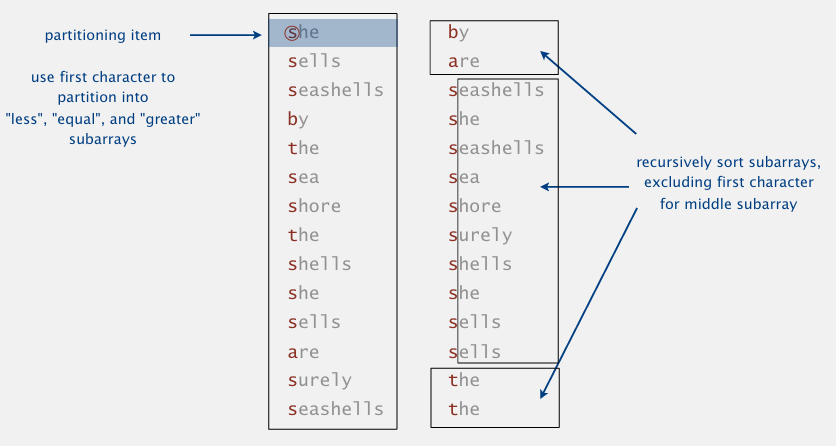
3-Way String Quicksort¶
public class Quick3string {
private static final int CUTOFF = 15; // cutoff to insertion sort
public static void sort(String[] a) {
StdRandom.shuffle(a);
sort(a, 0, a.length-1, 0);
}
// return the dth character of s, -1 if d = length of s
private static int charAt(String s, int d) {
if (d == s.length()) return -1;
return s.charAt(d);
}
// 3-way string quicksort a[lo..hi] starting at dth character
private static void sort(String[] a, int lo, int hi, int d) {
// cutoff to insertion sort for small subarrays
if (hi <= lo + CUTOFF) {
insertion(a, lo, hi, d);
return;
}
int lt = lo, gt = hi;
int v = charAt(a[lo], d);
int i = lo + 1;
while (i <= gt) {
int t = charAt(a[i], d);
if (t < v) exch(a, lt++, i++);
else if (t > v) exch(a, i, gt--);
else i++;
}
// a[lo..lt-1] < v = a[lt..gt] < a[gt+1..hi].
sort(a, lo, lt-1, d);
if (v >= 0) sort(a, lt, gt, d+1);
sort(a, gt+1, hi, d);
}
// exchange a[i] and a[j]
private static void exch(String[] a, int i, int j) {
String temp = a[i];
a[i] = a[j];
a[j] = temp;
}
}