基于物理的着色实践¶
在 SIGGRAPH 2014 中提到 PBR 包括材质、光源、相机三部分。1
由于实时渲染对帧率有要求,所以下面这些只是基于物理的实现,不是物理准确的实现。
材质¶
参考 glTF™ 2.0 Specification 中的实现,metallic-roughness 参数的 Cook-Torrance BRDF。
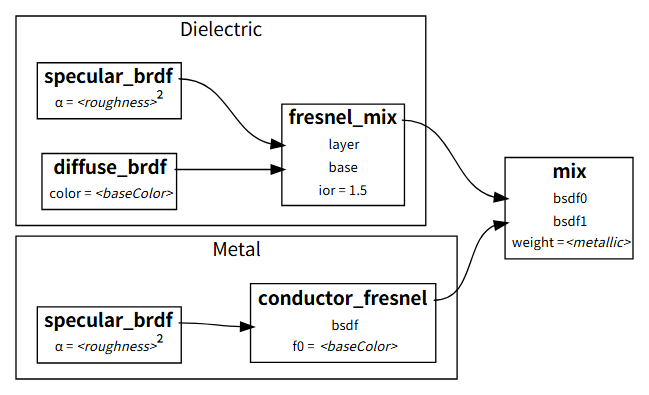
介电质¶
介电质(Dielectric)的 BRDF 分为 Diffuse 和 Specular 两部分,Diffuse 使用 Lambertian 模型,Specular 使用 Microfacet 模型。Unreal 在 2013 年指出,基于 Lambertian 的 Diffuse 模型对于实时渲染来说已经足够了。2
闫令琪表示:Combining a Microfacet BRDF with a diffuse lobe
- COMPLETELY WRONG
- COULDN'T BE WORSE
- I NEVER TAUGHT YOU SO
使用 Fresnel 来混合 Diffuse 和 Specular。IOR 固定使用 \(1.5\),对于大多数不透明的介电质材料来说,这是一个较好的折衷方案。具体实现时,Fresnel 采用 Schlick's approximation
float3 F_Schlick(float3 f0, float3 f90, float cosTheta)
{
float x = 1.0 - cosTheta;
float x2 = x * x;
float x5 = x2 * x2 * x;
return (f90 - f0) * x5 + f0;
}
其中 \(F_{90}\) 一般取 \(1\),而 \(F_0\) 可以根据 IOR 计算
金属¶
金属(Metal)会反射大部分光,只有少部分光会被吸收,所以只考虑 Specular。
同一种物质,对于不同波长光的 IOR 是不一样的,所以才有光的色散现象。只是对于介电质来说,这种变化的幅度通常比较小,所以就用一个数字来表示。但是对于金属来说,IOR 的变化就不能忽略了,通常要分别记录 RGB 三种光的 IOR,所以对应 Fresnel 的 \(F_0\) 也有三个不同的分量。

为了减少 PBR 材质对外暴露的参数数量,将金属的 \(F_0\) 存进 BaseColor 中(因为金属没有 Diffuse,所以 BaseColor 空出来了)。
实现¶
微表面模型中,NDF 使用 GGX,代码中 a2 是 \(\alpha^2\)
float D_GGX(float a2, float NoH)
{
float d = (NoH * a2 - NoH) * NoH + 1.0; // 2 mad
return a2 / (PI * d * d); // 4 mul, 1 rcp
}
Visibility 项使用高度相关(Height-Correlated)的 Smith Shadowing-Masking
float V_SmithJointGGX(float a2, float NoV, float NoL)
{
float smithV = NoL * sqrt(NoV * (NoV - NoV * a2) + a2);
float smithL = NoV * sqrt(NoL * (NoL - NoL * a2) + a2);
return 0.5 * rcp(smithV + smithL + FLT_EPS); // 必须加 epsilon,避免除以 0
}
GGX 中的粗糙度 \(\alpha=\text{roughness}^2\),roughness 是材质对外暴露的粗糙度参数。这是 Disney 提出的参数化方法,可以使粗糙度的变化在感知上更加线性。
介电质和金属的 BRDF 是根据金属度(metallic)参数混合的。由于两种 BRDF 中很多计算是相似的,所以很多地方可以合并,代码量很少。
struct BRDFData
{
float3 albedo;
float metallic;
float a2;
};
float3 MyBRDF(BRDFData data, float NoV, float NoL, float NoH, float LoH)
{
float3 f0 = lerp(0.04, data.albedo, data.metallic);
float3 F = F_Schlick(f0, 1.0, LoH);
float3 diffuseAlbedo = lerp(data.albedo, 0, data.metallic);
float3 diffuseTerm = (1.0 - F) * diffuseAlbedo / PI;
float3 specularTerm = F * D_GGX(data.a2, NoH) * V_SmithJointGGX(data.a2, NoV, NoL);
return diffuseTerm + specularTerm;
}
因为只计算法线半球,所以代码中 NoV、NoL、NoH、LoH 都要 saturate。
光源¶
光源强度使用物理单位,强度的衰减尽量接近物理规律。物理单位的选择基于 辐射度量学与光度学。
方向光¶
光源强度的单位使用 Lux,初始值通常是 \(\pi\)。用 \(\pi\) 当初始值,可能是因为漫反射项中有个除以 \(\pi\) 的操作,这样两个 \(\pi\) 抵消,变成 \(1\)。
精确光¶
精确光(Punctual light)指从一个点发光的光源。光源强度的单位通常使用 Candela 和 Lumen,传入 Shader 时统一转换成 Candela,算出光源的 立体角 就能转换。
对于一个着色点,方向光和精确光只有一个入射方向,所以反射方程可以化简,不需要积分。
点光源¶
点光源强度的衰减遵循平方反比定律
这个公式物理上正确,但存在一些问题
- 当 \(d\) 较小时,会非常亮
- 当 \(d\) 无穷大时,强度才衰减为 \(0\),这意味着场景中所有物体都要受到该光源影响,非常影响性能
Unreal 在 2013 年提出了一个衰减函数,在尽可能接近平方反比的同时解决上述问题 2
其中,\(r\) 是光源的衰减半径。分母中加 \(1\) 是为了避免 \(d\) 较小时光太亮。当 \(d>r\) 时,光强就会衰减到 \(0\)。
点光源的立体角是 \(4\pi\),所以
聚光灯¶
聚光灯要同时考虑距离衰减和夹角衰减,总衰减等于两者的乘积。距离衰减使用前面点光源的公式。
Unreal 的聚光灯有一个内锥角和一个外锥角,内锥角内没有夹角衰减,从内锥角到外锥角这个范围内,强度不断衰减,当角度大于外锥角时强度衰减为 \(0\)。
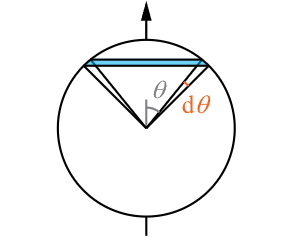
如下图所示,\(\theta_\text{inner}\) 是内锥角,\(\theta_\text{outer}\) 是外锥角,这两个角度都是圆锥顶角的一半。\(\theta\) 是着色点和聚光灯方向的夹角。
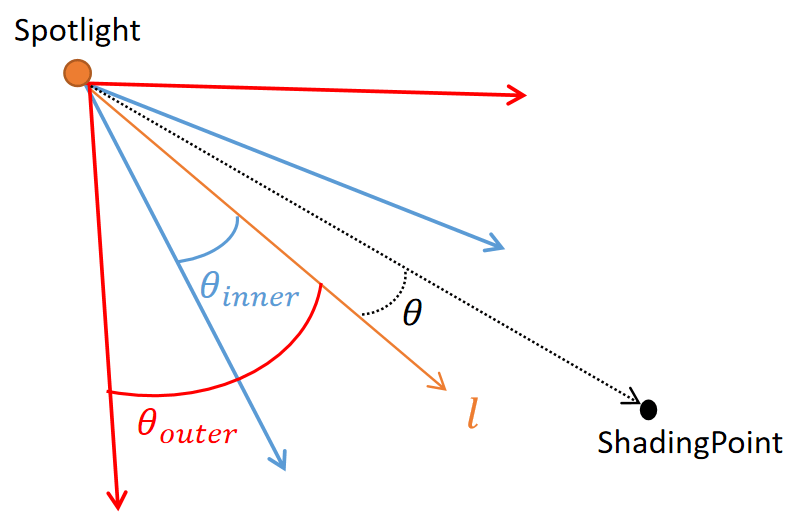
夹角衰减的公式为
聚光灯的立体角要用定义来计算,等于球冠的面积除以衰减半径的平方。将球冠划分为许多细圆环,然后积分
所以
面光源¶
LTC 方法。
光源强度的单位通常使用 Nit。
TODO
色温¶
通过 色温 来指定光源的颜色。
早期的 HDRP 代码中有色温到颜色的近似转换函数。3 色温范围是 \([1000,40000]\),单位是 Kelvin,返回的是线性的 RGB 颜色。
// TODO: Do a cheaper fitting
// Given a correlated color temperature (in Kelvin), estimate the RGB equivalent. Curve fit error is max 0.008.
// return color in linear RGB space
public static Color CorrelatedColorTemperatureToRGB(float temperature)
{
float r, g, b;
// Temperature must fall between 1000 and 40000 degrees
// The fitting require to divide kelvin by 1000 (allow more precision)
float kelvin = Mathf.Clamp(temperature, 1000.0f, 40000.0f) / 1000.0f;
float kelvin2 = kelvin * kelvin;
// Using 6570 as a pivot is an approximation, pivot point for red is around 6580 and for blue and green around 6560.
// Calculate each color in turn (Note, clamp is not really necessary as all value belongs to [0..1] but can help for extremum).
// Red
r = kelvin < 6.570f ? 1.0f : Mathf.Clamp((1.35651f + 0.216422f * kelvin + 0.000633715f * kelvin2) / (-3.24223f + 0.918711f * kelvin), 0.0f, 1.0f);
// Green
g = kelvin < 6.570f ?
Mathf.Clamp((-399.809f + 414.271f * kelvin + 111.543f * kelvin2) / (2779.24f + 164.143f * kelvin + 84.7356f * kelvin2), 0.0f, 1.0f) :
Mathf.Clamp((1370.38f + 734.616f * kelvin + 0.689955f * kelvin2) / (-4625.69f + 1699.87f * kelvin), 0.0f, 1.0f);
// Blue
b = kelvin > 6.570f ? 1.0f : Mathf.Clamp((348.963f - 523.53f * kelvin + 183.62f * kelvin2) / (2848.82f - 214.52f * kelvin + 78.8614f * kelvin2), 0.0f, 1.0f);
return new Color(r, g, b, 1.0f);
}
HDRP 后来改用 C++ 实现的 Mathf.CorrelatedColorTemperatureToRGB。
Light intensities¶
Unity 在 HDRP 文档中给出了一些光源强度的参考值。
Natural¶
Light measurements from natural sources in different conditions:
| Illuminance (lux) | Natural light level |
|---|---|
| 120 000 | Very bright sunlight. |
| 110 000 | Bright sunlight. |
| 20 000 | Blue sky at midday. |
| 1 000 - 2 000 | Overcast sky at midday. |
| < 1 | Moonlight with a clear night sky. |
| 0.002 | Starry night without moonlight. Includes airglow. |
Artificial¶
Approximate light measurements from artificial sources:
| Luminous flux (lumen) | Source |
|---|---|
| 12.57 | Candle light. |
| < 100 | Small decorative light, such as a small LED lamp. |
| 200 - 300 | Decorative lamp, such as a lamp that does not provide the main lighting for a bright room. |
| 400 - 800 | Ceiling lamp for a regular room. |
| 800 - 1 200 | Ceiling lamp for a large brightly lit room. |
| 1 000 - 40 000 | Bright street light. |
Indoor¶
Architects use these approximate values as a guide when designing rooms and buildings for functional use:
| Illuminance (lux) | Room type |
|---|---|
| 150 - 300 | Bedroom. |
| 300 - 500 | Classroom. |
| 300 - 750 | Kitchen. |
| 300 - 500 | Kitchen Counter or Office. |
| 100 - 300 | Bathroom. |
| 750 lux - 1 000 | Supermarket. |
| 30 | City street at night. |
For more examples of indoor light levels see Archtoolbox’s web page on Recommended Lighting Levels in Buildings.
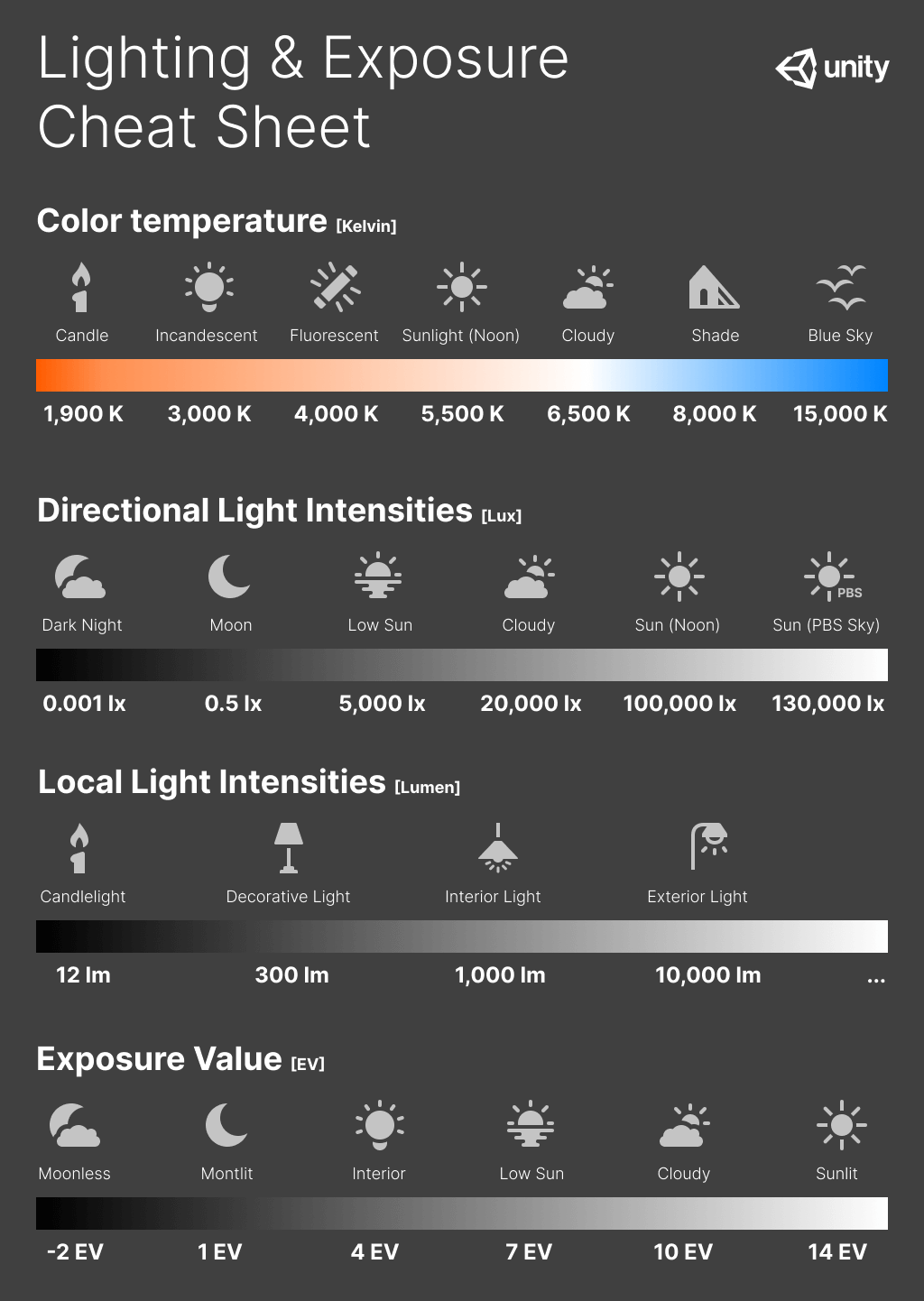
Lighting and exposure diagram¶
The following cheat sheet contains the color temperature values and light intensities of common real-world Light sources. It also contains Exposure values for different illumination scenarios.
相机¶
还没做,但收集了一些资料
- HDRP camera component reference | High Definition RP | 17.0.4
- Unity - Manual: Physical Camera Inspector window reference for URP
- Unity - Manual: Using Physical Cameras(一些参数解释得比较清楚)
还有后期自动曝光(后处理中的 Exposure)也要了解。
参考¶
- 游戏引擎编程实践(6)- 精确光源和面光源的实现 - 知乎
- [HDRP]物理灯光是什么?科普向 - 知乎
- Physical light units | High Definition RP | 14.0.12
- glTF™ 2.0 Specification
- LearnOpenGL - Theory
-
Lagarde S, De Rousiers C. Moving frostbite to physically based rendering 3.0[J]. SIGGRAPH Course: Physically Based Shading in Theory and Practice, 2014, 3. ↩
-
Karis B, Games E. Real shading in unreal engine 4[J]. Proc. Physically Based Shading Theory Practice, 2013, 4(3): 1. ↩↩
-
Graphics/com.unity.render-pipelines.high-definition/Runtime/Lighting/LightUtils.cs at 5.2.0 · Unity-Technologies/Graphics ↩